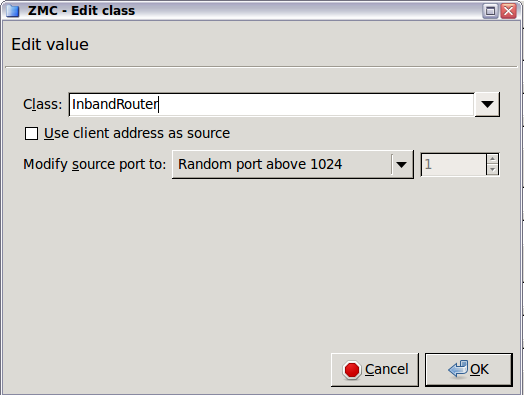
The InbandRouter determines the target address from the information embedded in the transferred protocol. This is possible only for protocols that can have routing information within the data stream. Zorp can use InbandRouter with the HTTP and FTP protocols.
The InbandRouter has the following options:
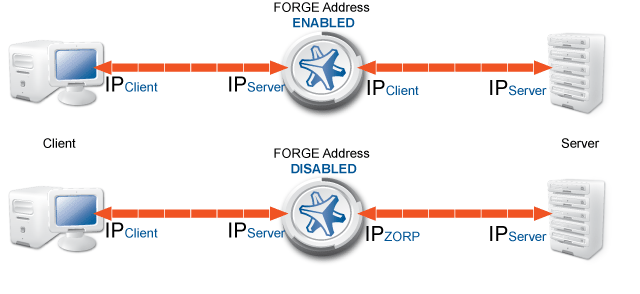
By default, Zorp uses its own IP address in the server-side connections: the server does not see the IP address of the original client. By selecting this option, Zorp mimics the original address of the client. Use this option if the server uses IP-based authentication, or the address of the client must appear in the server logs.
| Note |
|---|
This option was called Forge address in earlier versions of Zorp. |
| Note |
|---|
The IP address of the client is related to the source NAT (SNAT) policy used for the service: using SNAT automatically enables the Use client address as source option in the router. |
This option defines the source port that Zorp uses in the server-side connection. The following options are available:
Random port above 1024: Select a random port between 1024 and 65535. This is the default behavior of every router.
Random port in the same group: Select a random port in the same group as the port used by the client. The following groups are defined: 0-513, 514-1024, 1025–.
Client port: Use the same port as the client.
Specified port: Use the port set in the spinbutton.
| Note |
|---|
This option was called Forge port in earlier versions of Zorp. |
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu