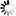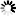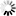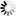12.5.3.2. Procedure – Configure additional Heartbeat parameters
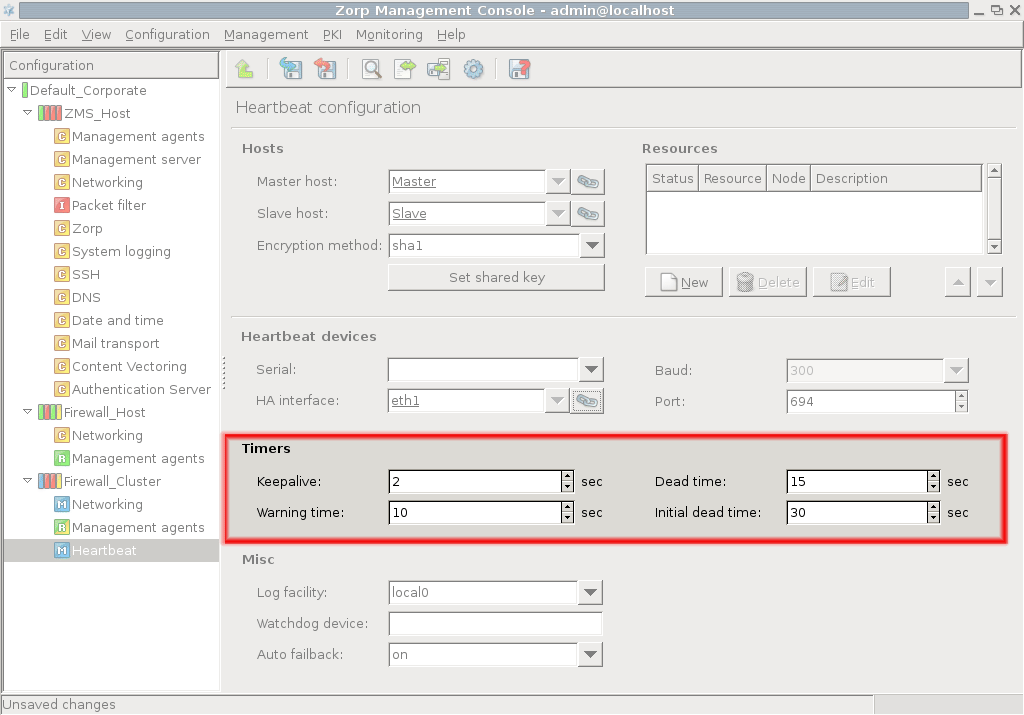
Set timers for Heartbeat in the section.
The following timers can be defined. Give all the values in seconds.
- keepalive
The interval in seconds between subsequent Heartbeat signals.
- warning time
The interval in seconds after which the slave node gives warning of the dead master node.
- dead time
The interval in seconds after which the node is assumed to be dead.
- initial dead time
First deadtime after system reboot in seconds.
Tip It may take a while in some machines to have a fully functional network after a reboot. It is recommended to set the dead time twice as long as the warning time, and the initial deadtime twice as long as the dead time. For example, if the warning time is 20 seconds, the optimal dead time is 40 seconds and the optimal initial dead time is 80 seconds.
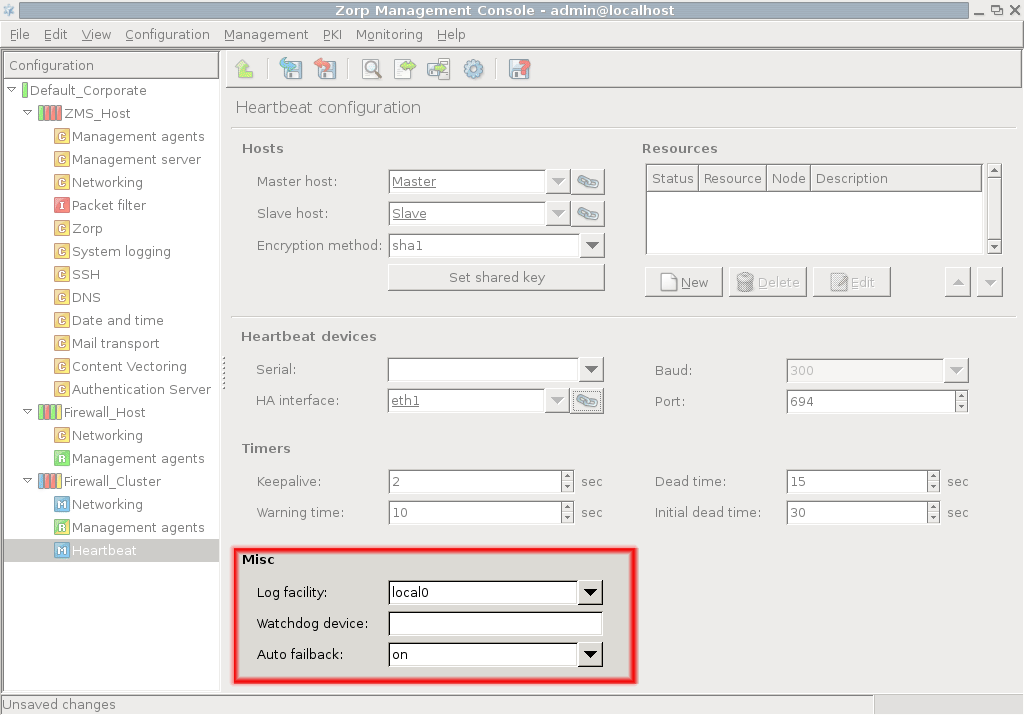
Set other Heartbeat options in the subwindow.
Select the log target, watchdog device and decide about service reacquiry in case of master node recovery.
- log facility
This option determines the target device for logging.
- watchdog
This option determines which watchdog device is used, if any. For example, /dev/watchdog.
Watchdogs can monitor the heartbeat messages of a node and reboot the node if it fails.
- nice fallback
This option prevents the master node from reacquiring cluster resources after a failover in case the master node gets functional again. Enabling
nice_failbackcan cause problems in certain situations. Suppose there is a two-node cluster with a master (Node_A) and a slave (Node_B) node. IfNode_Afails,Node_Bacquires its resources and uses a STONITH device to power off theNode_A. WhenNode_Arecovers, the resources remain onNode_Bifnice_failbackis enabled. However, if nowNode_Bseems to fail,Node_Acan power offNode_Bonly if two STONITH devices are intalled to the system (one to power offNode_A, one to power offNode_B).Tip It is recommended to enable
nice_failback, but after a takeover restore the original master-slave node hierarchy at the earliest possible time (for example, during the next maintenance break).
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu