By default, ZMC defines a zone called internet on every site. The internet contains the 0.0.0.0 and the ::0 networks with the 0 subnet mask. This zone means any network: every IP address not belonging to any other zone belongs to the internet zone.
| Note |
|---|
Zorp uses the CIDR notation for subnetting. |
The internet zone is typically used in firewall rules where one side of the connection cannot be defined more exactly.
| Example 6.1. Using the Internet zone |
|---|
The Internet zone identifies all external networks. To allow the internal users to visit all web pages, simply set the destination zone of the HTTP service to |
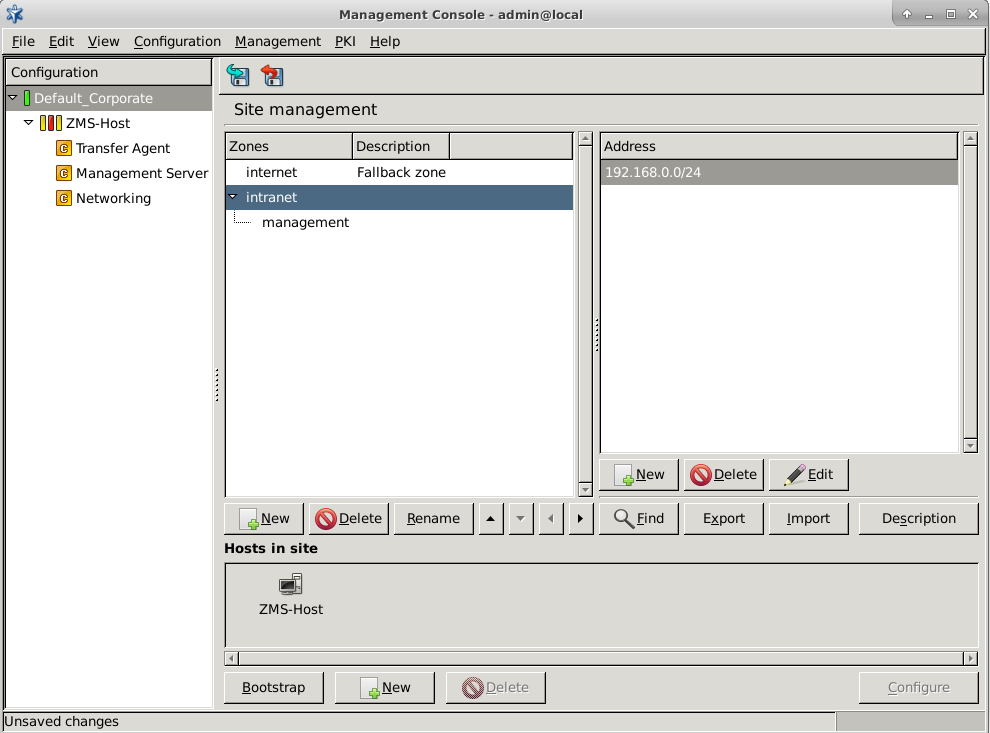
Zones are managed on the component in ZMC. The left side of the main workspace displays the zones defined on the site and their descriptions. IP networks that belong to the selected zone are displayed on the right side of the workspace.
| Note |
|---|
The ZMC component has a shortcut in its icon bar to the zone editor. The zone hierarchy applies to all firewalls of the site, therefore carefully consider every modification and its possible side-effects. |
Use the control buttons to create, delete, or edit the zone definitions and the IP networks. Use the arrow icons to organize the zones into a hierarchy (see Section 6.2.3, Zone hierarchies for details).
If a zone is created, modified or deleted in a ZMC, the change is immediately visible in the zone lists of the same ZMC without committing the changes. If these changes to a zone or zones are committed, the changes become visible in the zone information of other ZMCs as well.
| Example 6.2. Subnetting |
|---|
|
Suppose you have the following IP address range to put into a zone: Furthermore, if you define Zone A with the IP network |
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu