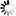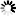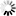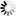ZAS instances using specific database backends can be configured in the section of the ZMC component. The existing instances and the type of database they use are displayed in a list; instances can be created, deleted, and modified using the control buttons below the list.
| Note |
|---|
Only unused instances can be deleted; if an instance is used in a router, the router has to be modified or deleted first. |
To create a new instance, complete the following procedure:
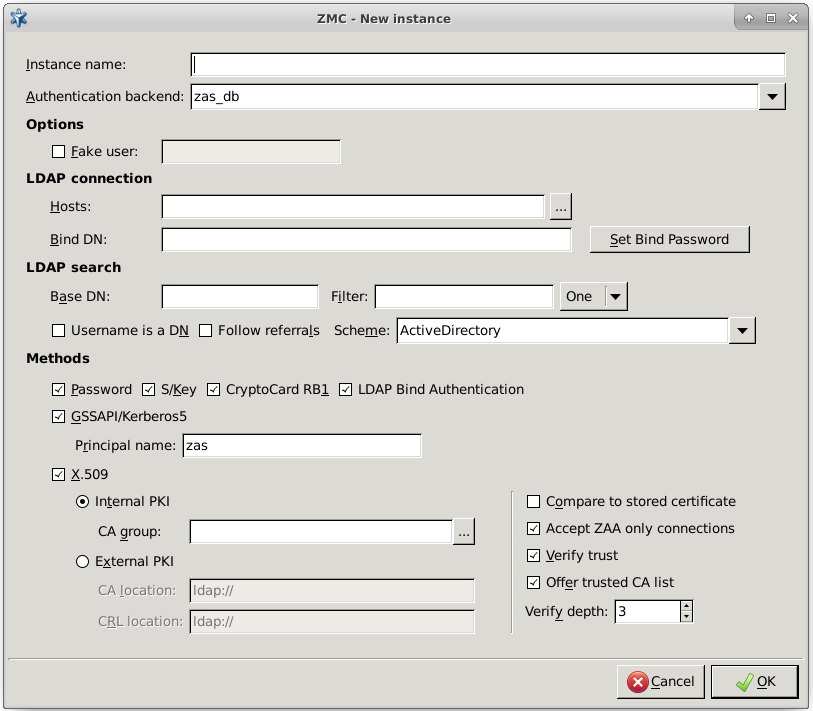
The zas_db backend authenticates users against an LDAP database using the Microsoft Active Directory, the POSIX, or the Novell eDirectory/NDS scheme.
The backend has the following settings:
: Enable authentication faking. This requires a valid user account in the LDAP database that is exclusively used for this purpose. The user name of this account has to be set in the corresponding textbox.
Note All backends are capable of authentication faking. This is a method to hide the valid usernames, so that they cannot be guessed (for example using brute-force methods). If somebody tries to authenticate with a non-existing username, the attempt is not immediately rejected: the full authentication process is simulated (for example, password is requested, and so on), and rejected only at the end of the process. That way it is not possible to determine if the username itself was valid or not. It is highly recommended to enable this option.
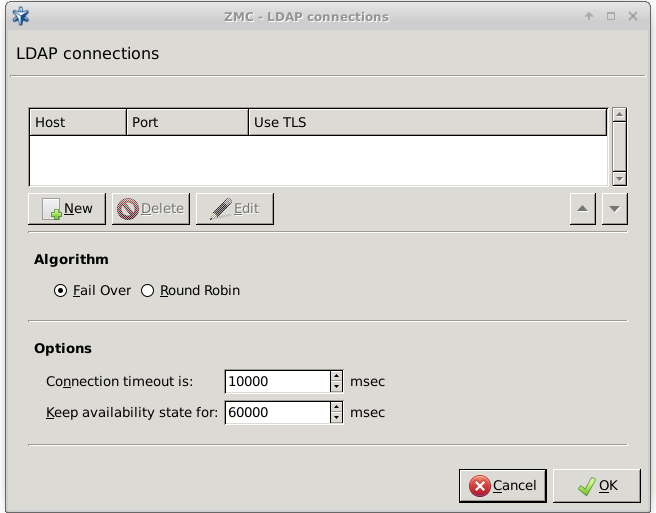
: By clicking on next to the host related information can be specified.
: It is the list of LDAP servers. To set the order of servers, use the arrow buttons below the list.
: It is the IP address of the LDAP server.
: It is the port number of the LDAP server.
: Enable TLS encryption to secure the communication between ZAS and the backend.
: ZAS attempts to connect to the next host in the ordered LDAP connections list based on the selected algorithm.
: Specifies connection timeout to be used when connecting to the target server.
: ZAS does not try to connect to an unreachable server until the time set in milliseconds in the Keep availability state for option expires.
: Bind to this DN before accessing the database.
: It shall be the password to use when binding to LDAP.
:
: Perform queries using this DN as base.
: Search for accounts using this filter expression.
: It specifies the scope of the search.
base,sub, andoneare acceptable values, specifyingLDAP_SCOPE_BASE,LDAP_SCOPE_SUB, andLDAP_SCOPE_ONE, respectively.: It indicates that the incoming username is a fully qualified DN.
: If this option is set, ZAS will respect the referral response from the LDAP server when looking up a user.
: Specify LDAP scheme to use:
Active Directory,POSIX, orNDSstyle directory layout.Note Make sure to set
SchemetoActive Directorywhen using a Microsoft Active Directory server as a database backend.
: Select and configure the allowed authentication methods.
: It implements password authentication. Allow password authentication only if the connection between Zorp and ZAS is secured (see Section 15.3.2, Authentication of Zorp services with ZAS for details).
: It is the S/Key-based authentication.
: It defines cryptoCard RB1 hardware token based authentication.
: It is authentication against the target LDAP server. Only password authentication is supported by this method, therefore it is only available if the connection between ZAS and Zorp is secured with SSL.
: It defines GSSAPI-based authentication. The representing this authentication service also has to be set.
: It is authentication based on x.509 certificates. To use this method, a number of further options have to be specified:
This can be an internal CA group (managed by the Zorp PKI, see Chapter 11, Key and certificate management in Zorp for details), or an external one. In the latter case the locations of the trusted CA certificates and the corresponding CRLs have to be set as space-separated lists of
file://orldap://URLs.: Compare the stored certificate bit-by-bit to the certificate supplied by the client. The authentication will fail when the certificates do not match, even if the new certificate is trusted by the CA.
: Verify the validity of the certificate (that is, the certificate has to be issued by one of the trusted CAs and must not be revoked). This verification is independent from the , so if both parameters are set, both conditions must be fulfilled to accept the certificate.
: The maximum length of the verification chain.
: Send a list of trusted certificates to the client to choose from to narrow the list of available certificates.
: By default, ZAS accepts connections only from Zorp Authentication Agents (ZAA). Disable this option if a different client is used to authenticate on ZAS, for example, if a web-browser authenticates using a client-side certificate.
Disabling this option works only with proxies that support inband authentication, for example, HTTP.
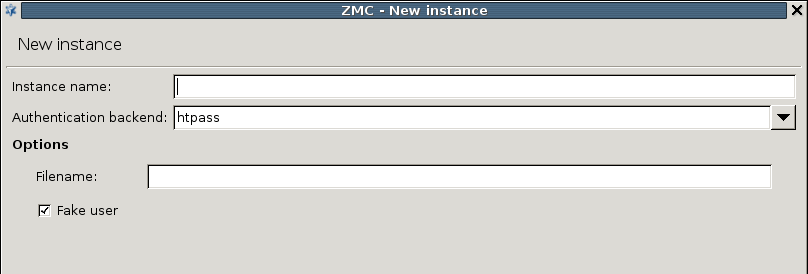
The backend authenticates users against an Apache htpasswd style password file. The name (including the path) of the file to be used has to be specified in the textbox. Authentication faking can be enabled by selecting the checkbox.
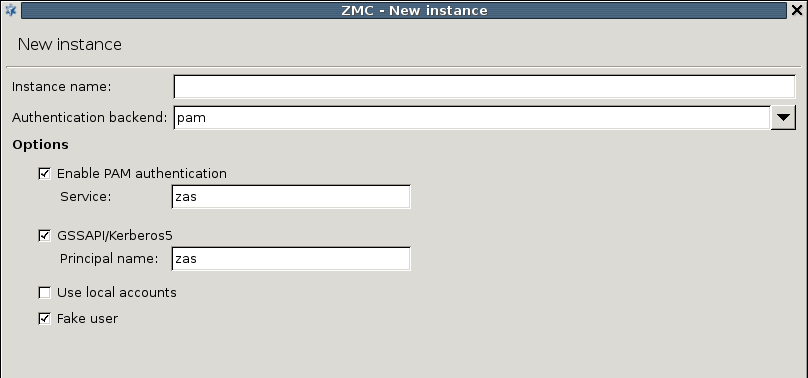
The PAM backend implements authentication based on the local authentication settings of the host running ZAS. It basically authenticates the users against the local PAM installation and/or using GSSAPI/Kerberos5.
The PAM backend has the following parameters:
: Enable PAM authentication. For PAM authentication the PAM service used for authentication has to be specified.
: Enable GSSAPI based authentication. The representing this authentication service also has to be set.
: Use the local passwd/group database to query group membership of a given account.
Authentication faking can be enabled by selecting the checkbox.
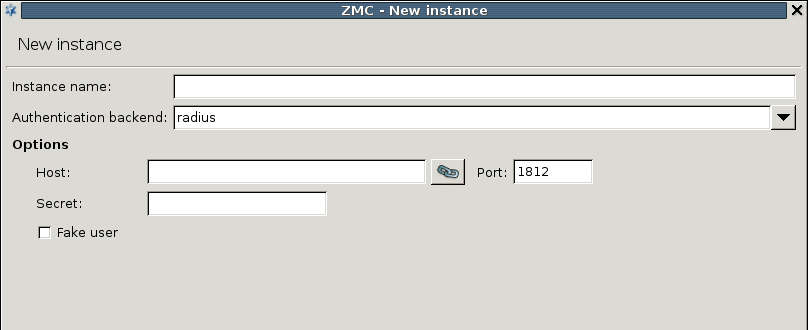
The RADIUS backend has the following parameters:
: It is the hostname of the RADIUS server.
: It is the port of the RADIUS server.
: It is the shared secret between the authentication server and ZAS.
Authentication faking can be enabled by selecting the checkbox.
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu