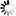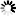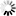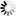5.3.1. Procedure – Configure name resolution
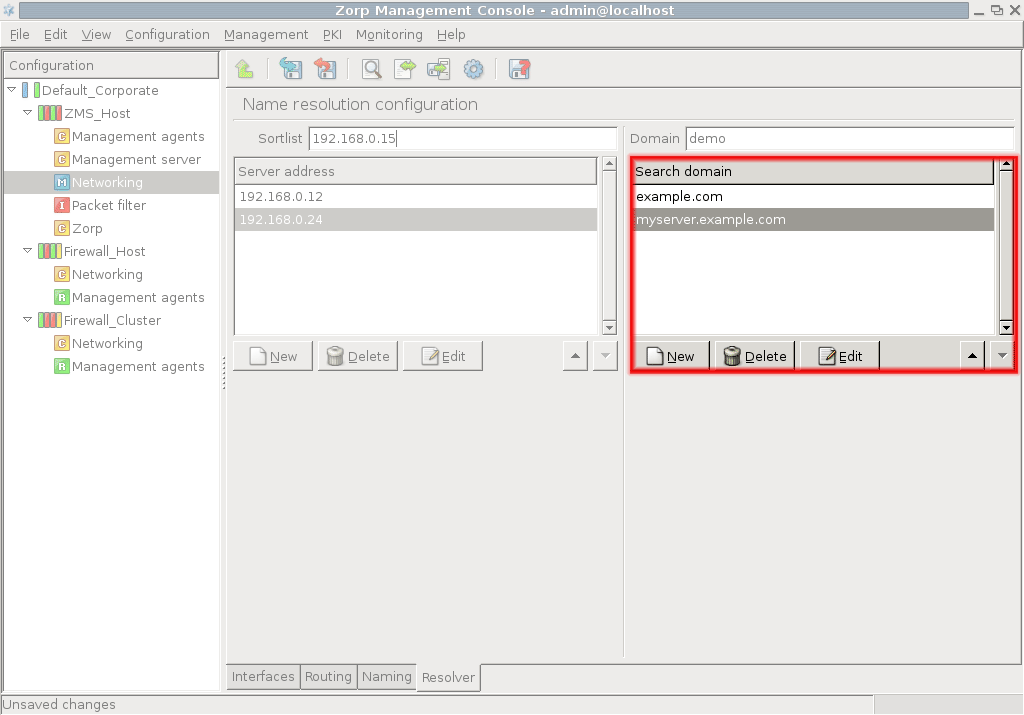
List the nameservers to be used by your host in the right pane.
Set a priority order among the nameservers. The first one on the list is queried first.
Set up domain search order in the left pane.
Use the buttons with triangles on the right.
This information is used when you issue a name query for a hostname but without supplying the domain name parts: for example, telnet myserver. In this case, the resolver automatically tries to append domain substitutes to the hostname in the order you specify, before sending queries to nameservers.
In the example above, this would be
example.comand then, if the query is unsuccessfulmyserver.example.com.OPTION
Define the preferred interface in the .
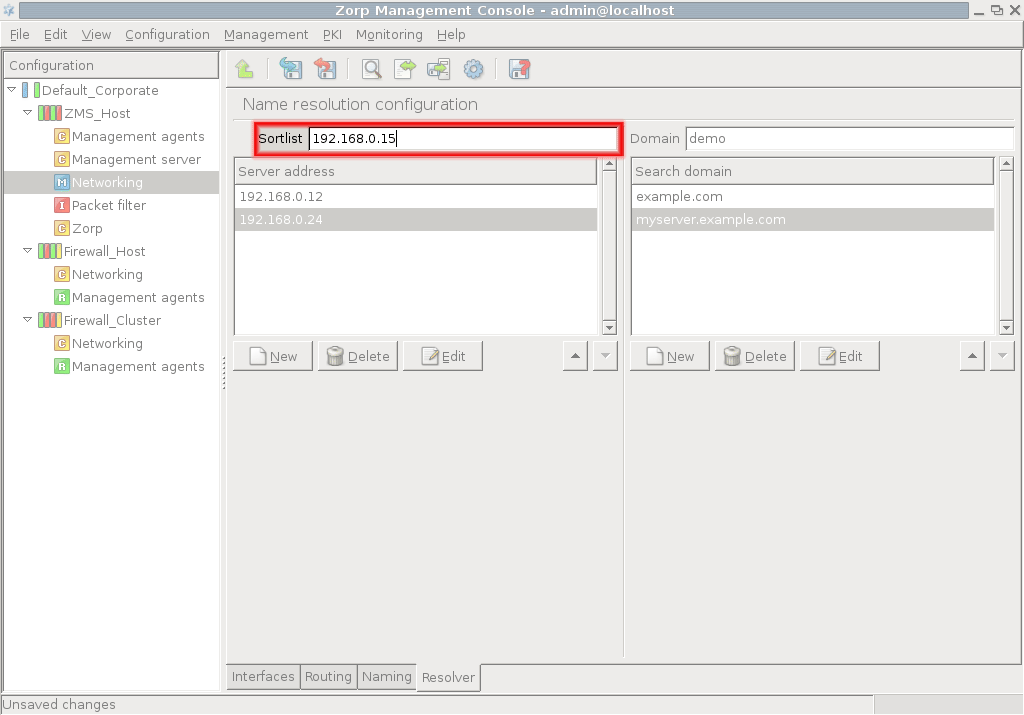
The sortlist directive specifies the preferred interface you wish to communicate on, when, as a result of a query, you receive more than one IP addresses for a given host. The value of Sortlist can be a network IP address or a host IP address/subnet mask pair, where the subnet mask is in the classic dotted decimal format and not in CIDR notation.
Tip The optimization using the Sortlist might be useful for firewalls with many interfaces installed, or in the following special network setup.
The firewall is connected to the Internet with two interfaces: one for a broadband, primary connection and another, lower-bandwidth backup connection through a different Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you want to reach a server on the Internet, the DNS query returns two IP addresses for the same server. From its routing table, your firewall deduces that both IP addresses are reachable, but by default it uses the IP address that was listed first in the DNS response, even if that IP address is reachable through the — slower — backup line. To avoid this situation, you can explicitly tell your resolver with the feature that whenever possible, it must prefer the interface that connects to the higher-bandwidth primary line.
Note that the feature provides just a preference and not an exclusive setting: if the targeted server cannot be reached via the interface designated by the sortlist parameter, the other interface(s) and IP addresses are tried.
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu