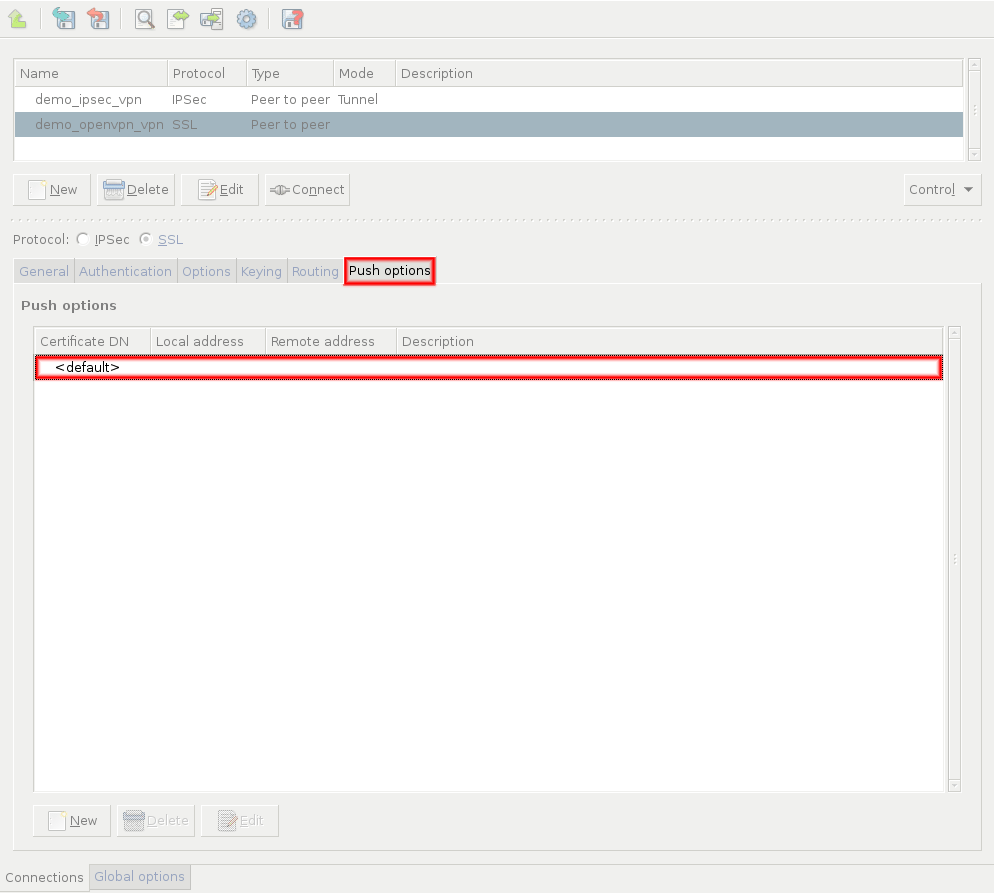
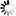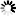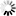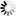Push options are settings that the remote clients can download from Zorp when the VPN tunnel is built.
To set push options that apply for every remote endpoint of the selected VPN connection, double-click the entry.
The following push options can be set on the tab:
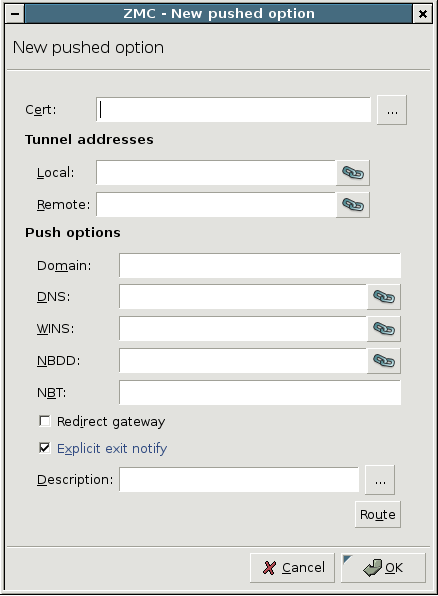
: It is the domain of the network.
: It denotes the address of the Domain Name Server (DNS).
: It is the address of the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) Server.
: It is the address of the NetBIOS Datagram Distribution (NBDD) Server.
: It is the type of the NetBIOS over TCP/IP node. Enter the number corresponding to the selected mode:
1: Send broadcast messages.
2: Send point-to-point name queries to a WINS server.
4: Send broadcast message and then query the nameserver.
8: Query name server and then send broadcast message.
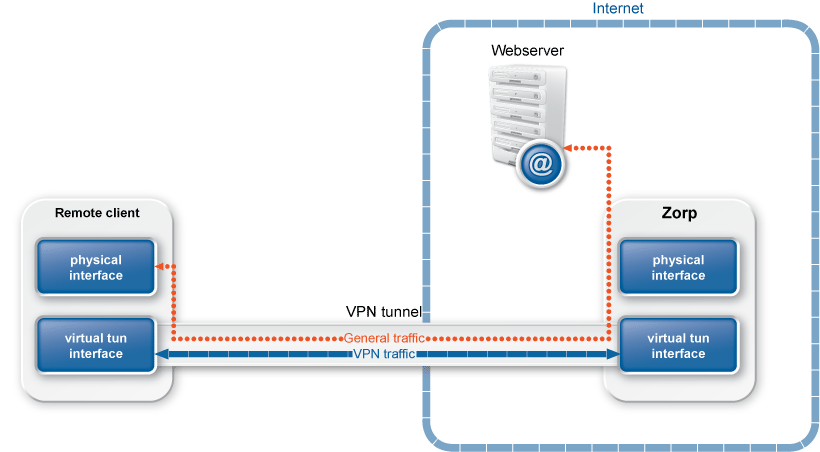
: It sends every network traffic of the remote endpoint through the VPN tunnel. See Section The Redirect gateway option for details.
Note Using the option means that the remote client will have access only to the services permitted by Zorp for the VPN tunnel when the VPN tunnel is active. For example, the client will not be able to surf the Internet using HTTP if Zorp allows only POP3 services for the clients connected using the VPN.
: The remote endpoint sends a message to Zorp before closing the VPN tunnel. If this option is disabled, Zorp does not immediately notice that an endpoint became unavailable, and error messages might appear in the Zorp logs.
: Enter any additional push options that need to be set here. Options entered here are automatically appended to the end of the
.ccdfile of the VPN tunnel. This option can be used for example to set theirouteparameter.: Add routing entries for the remote endpoint. These routing entries determine which networks protected by Zorp are accessible from the remote endpoint.
To set push options for a specific remote endpoint, click and select the certificate of the remote endpoint.
| Note |
|---|
Alternatively, enter the Unique Name of the endpoint certificate into the field. That way, certificates not available in the Zorp PKI system can be used as well. |
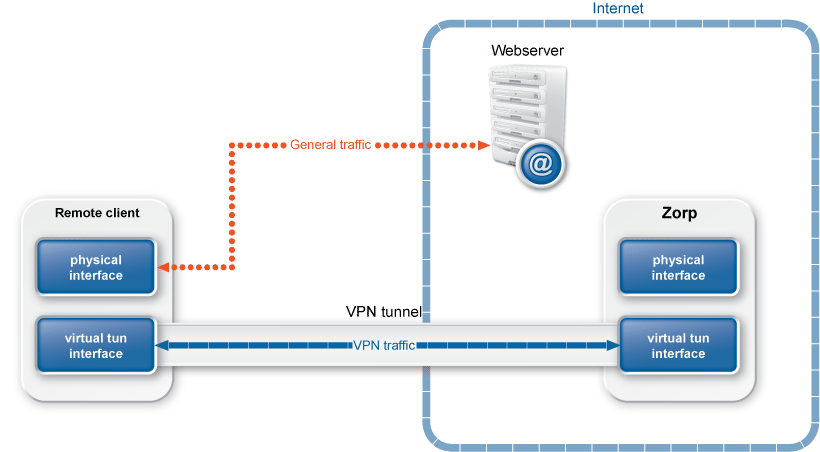
In this case, the IP addresses visible in the tunnel can also be set, so a fixed IP address can be assigned to the client using the parameter. Note that the and directions are from the client's perspective: is the remote client's IP address in the VPN tunnel, while is the IP address of Zorp in the VPN tunnel.
When assigning fixed IP addresses to Windows clients, remember that every Windows client needs a /30 netmask (4 IP addresses). For every client, use an IP pair of the following list as the last octet of the and IP addresses:
[ 1, 2] [ 5, 6] [ 9, 10] [ 13, 14] [ 17, 18] [ 21, 22] [ 25, 26] [ 29, 30] [ 33, 34] [ 37, 38] [ 41, 42] [ 45, 46] [ 49, 50] [ 53, 54] [ 57, 58] [ 61, 62] [ 65, 66] [ 69, 70] [ 73, 74] [ 77, 78] [ 81, 82] [ 85, 86] [ 89, 90] [ 93, 94] [ 97, 98] [101,102] [105,106] [109,110] [113,114] [117,118] [121,122] [125,126] [129,130] [133,134] [137,138] [141,142] [145,146] [149,150] [153,154] [157,158] [161,162] [165,166] [169,170] [173,174] [177,178] [181,182] [185,186] [189,190] [193,194] [197,198] [201,202] [205,206] [209,210] [213,214] [217,218] [221,222] [225,226] [229,230] [233,234] [237,238] [241,242] [245,246] [249,250] [253,254]
Enabling the push-option overrides the default gateway settings of the remote endpoint and sends every network traffic of the remote endpoint through the VPN tunnel. The remote endpoint can only access the Internet through the VPN tunnel. That way Zorp can control what kind of communication (protocols, and so on) can the remote client use while connected to the internal network using the VPN tunnel.
The following flags can be set for the option, with the being set as default:
: Select this option if the end-points of the VPN tunnel are directly connected through a common subnet, such as wireless. Note that in this case Zorp does not create a static route for the remote address of the tunnel.
: Select this option to add a direct route to the DHCP server (if it is non-local) which bypasses the VPN tunnel.
: Select this option to override the default gateway by using
0.0.0.0/1and128.0.0.0/1instead of0.0.0.0/0. That way the original default gateway is overridden but not deleted.: Select this option to add a direct route to the DNS server(s) (if it is non-local) which bypasses the VPN tunnel.
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu