Configuration files:
 provides further information and configuration options of the files and attributes described in the output window of and the diff command.
provides further information and configuration options of the files and attributes described in the output window of and the diff command.
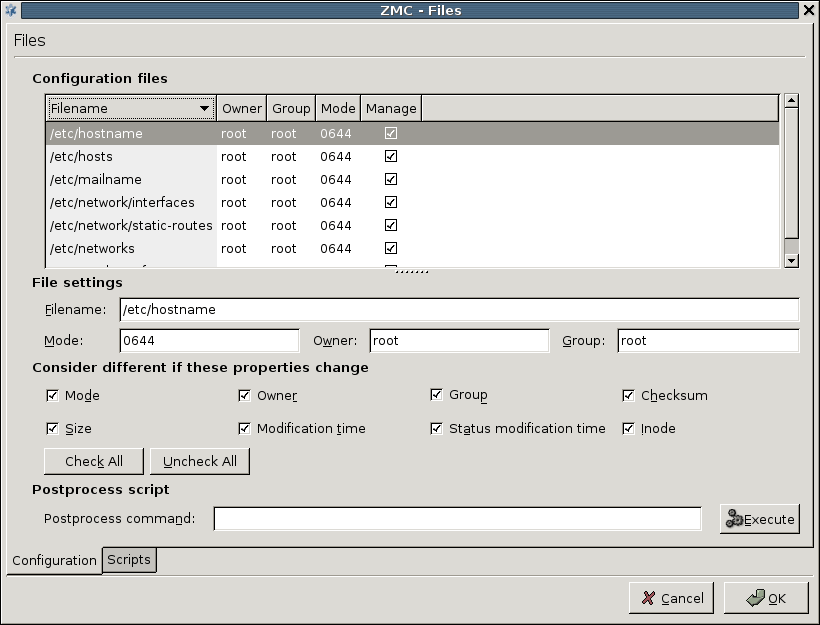
serves two purposes.: It provides vital information about which configuration files a component (of the tree) uses and gives chance to modify the properties of the listed files.
For example, in case of the Networking component, the list of used files is the following.
Apart from the name and location of files, information can be retrieved about the owner, owner group, access rights and file type parameters. The column is very important and has a corresponding checkbox immediately below the file listing: this can be used to control what files ZMS manipulates on the host machine, if needed.
| Note |
|---|
It is not recommended to take files out of the authority of ZMS, because it can severely limit the effectiveness of ZMS–based administration. However, it is possible to do it, if the checkbox under the column is deselected. |
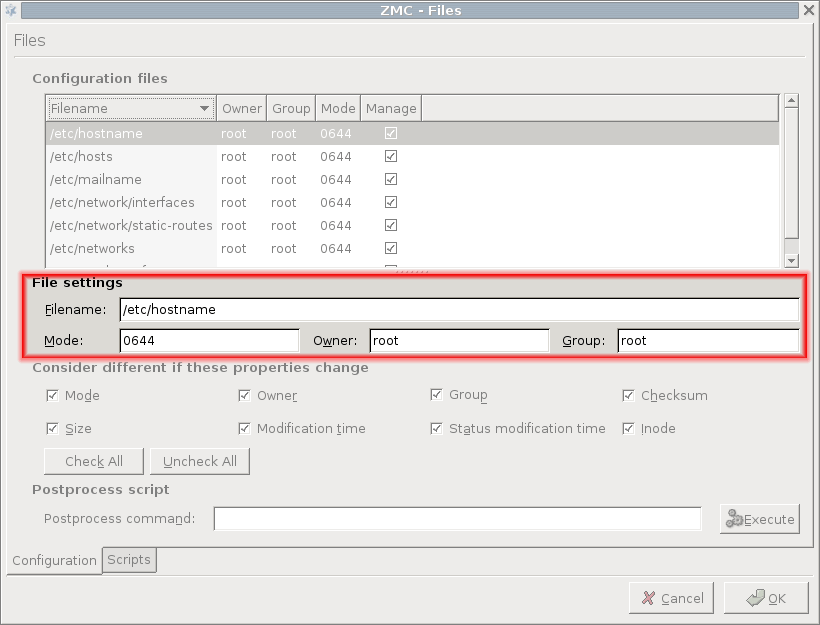
File settings:
To modify the properties of a file, click on the file in the list. The following subwindow opens.
| Warning |
|---|
There must be a solid reason for changing these properties and one must be prepared for the possible consequences of such actions. A good understanding of Linux is recommended before making changes in file properties. |
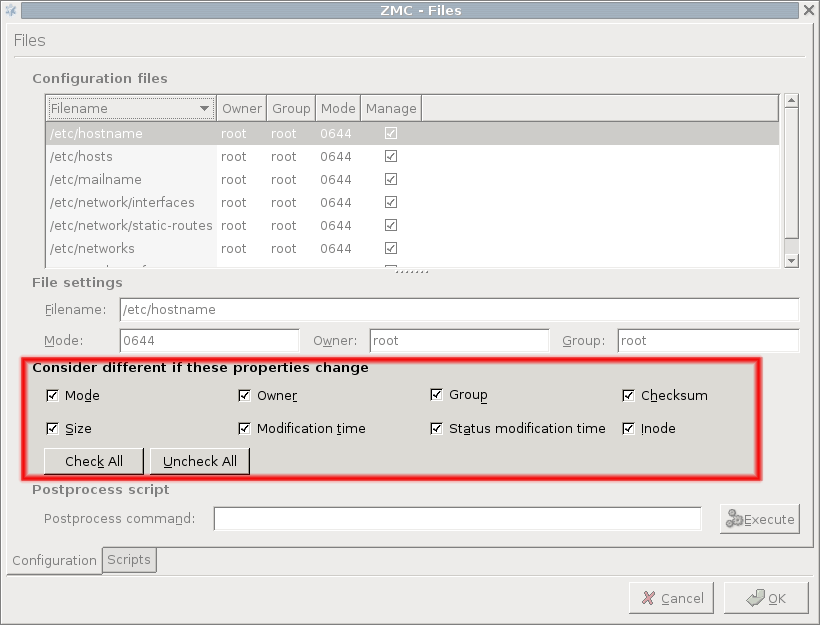
Consider different if these properties change:
The third part of the window is for configuring the work of the comparison utility, which is diff by default. It can be defined which file properties are required when checking for changes.
| Tip |
|---|
Checking for configuration file differences is beneficial from a security aspect too: it is an additional tool for making sure nobody has altered critical files on the firewall. |
Postprocess script:
At the bottom of the tab, a postprocess command can be specified that is run after the corresponding configuration file is uploaded to the firewall host. Some services rely heavily on this option. For example, Postfix that runs /usr/sbin/postmap %f as a postprocess command to transport virtual domains and set various access restrictions are properly.
Scripts tab:
Configuration files under Linux are reread during service reloads or restarts. These actions are performed by running the corresponding scripts exclusively from the /etc/init.d directory. The tab of the window provides an interface where the starting scripts can be checked and alter and fine-tune them with special Pre upload and Post upload commands. With simple components, such as Networking, these options are rarely used, but in some cases might prove especially useful.
Some components, for example, , can manage configuration files that are automatically reloaded. They cannot be restarted after a . To set the status icon of these components to , select on the tab.
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu