| Note |
|---|
|
Packet filtering rules are created and managed automatically by ZMS. Usually it is not required nor recommended to modify them manually. If the transfer of traffic is required without application-level inspection, create a packet filter service (see Procedure 6.4.1, Creating a new service for details). To enable access to services running on firewall hosts (e.g., SSH access), see Section 9.4, Local services on Zorp. Typically, the packet filtering rules have to be modified when traffic without terminating it on Zorp has to be forwarded, like forwarding IPSec VPN connections. |
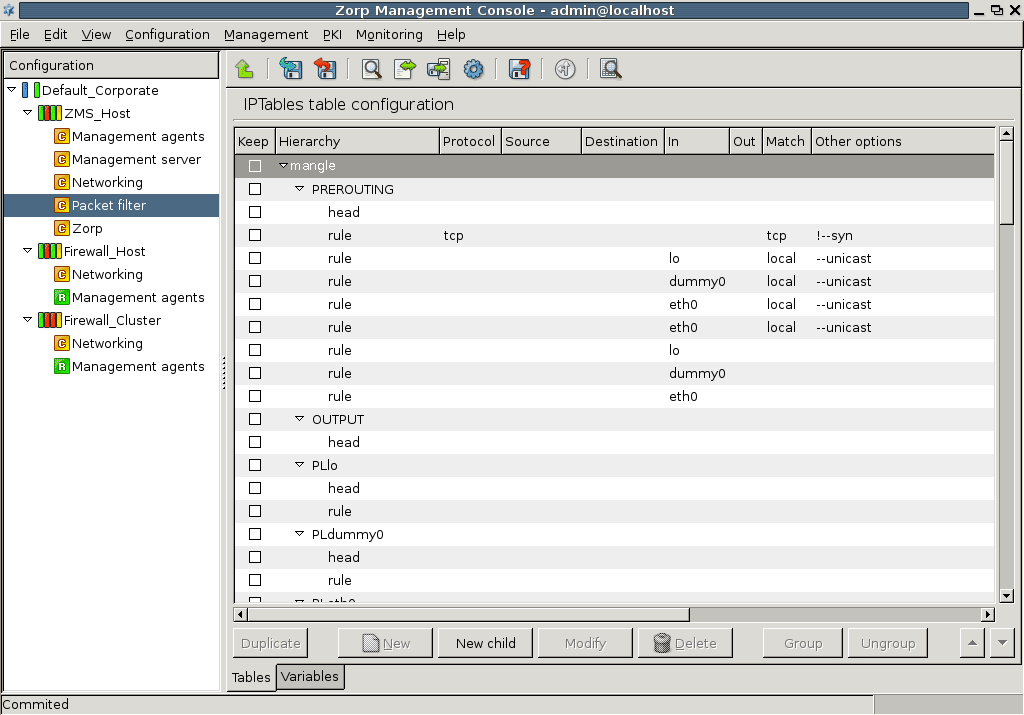
ZMC provides an easy and comfortable way to configure the packet filter system on managed hosts. To configure the packet filter the component must be added to the managed host. The default configuration defines a default deny/drop setup which means that all packets are dropped and logged in the filter table on the INPUT and FORWARD chains since it is enough to disable all passing traffic on the firewall and there is no need to have drop rules on any other chains. By default, the policy permits all outgoing packets.
To use the Packet Filter component a basic (but preferably higher) understanding of Netfilter/IPTables is required. This component has three basic purposes:
add/delete/modify rules,
generate configuration, and
search/review the ruleset.
Creating all of the packet filter rules for the firewall and keeping the ruleset in synchrony with Zorp is a very challenging and time-consuming task therefore the manual configuration is assisted by a feature which generates the ruleset of the policy. Using this feature of generating the ruleset does not raise any boundaries, neither limits the administration and does not render the configuration inflexible either. The generated policy is just a skeleton which can be modified as any ordinary ruleset.
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu