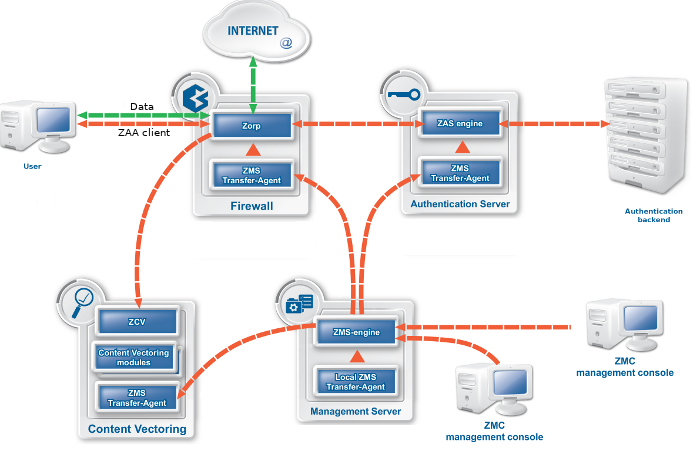
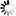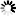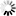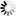A typical Zorp Gateway solution consists of the following components:
One or more Zorp firewall hosts. Zorp is inspecting and analyzing all connections.
A Zorp Management Server (ZMS)
ZMS is the central managing server of the Zorp Gateway solution. ZMS stores the settings of every component, and generates the configuration files needed by the other components. A single ZMS can manage the configuration of several Zorp firewalls — for example, if an organization has several separate facilities with their own firewalls, each of them can be managed from a central Zorp Management Server.
One or more desktop computers running the Zorp Management Console (ZMC), the graphical user interface of ZMS
The Zorp administrators use this application to manage the entire system.
Transfer agents
These applications perform the communication between ZMS and the other components.
One or more Zorp Content Vectoring System (ZCV) servers
ZCV servers can inspect and filter the content of the network traffic, for example, using different virus- and spamfiltering modules. ZCV can inspect over 10 network protocols, including encrypted ones as well. For example, SMTP, HTTP, HTTPS, and so on.
One or more Zorp Authentication Server (ZAS)
ZAS can authenticate every network connection of the clients to a variety of databases, including LDAP, RADIUS, or TACACS. Clients can also authenticate out-of-band using a separate authentication agent.
| Note |
|---|
| The name of the application effectively serving as the Zorp component of Zorp Professional is Zorp, commands, paths and internal references will relate to that naming. |
The following figure shows how these components operate:
Published on May 30, 2024
© BalaSys IT Ltd.
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu