16.3.1. Procedure – Configuring IPSec connections
Navigate to the VPN component of the PNS host that will be the endpoint of the VPN connection. Select the tab.
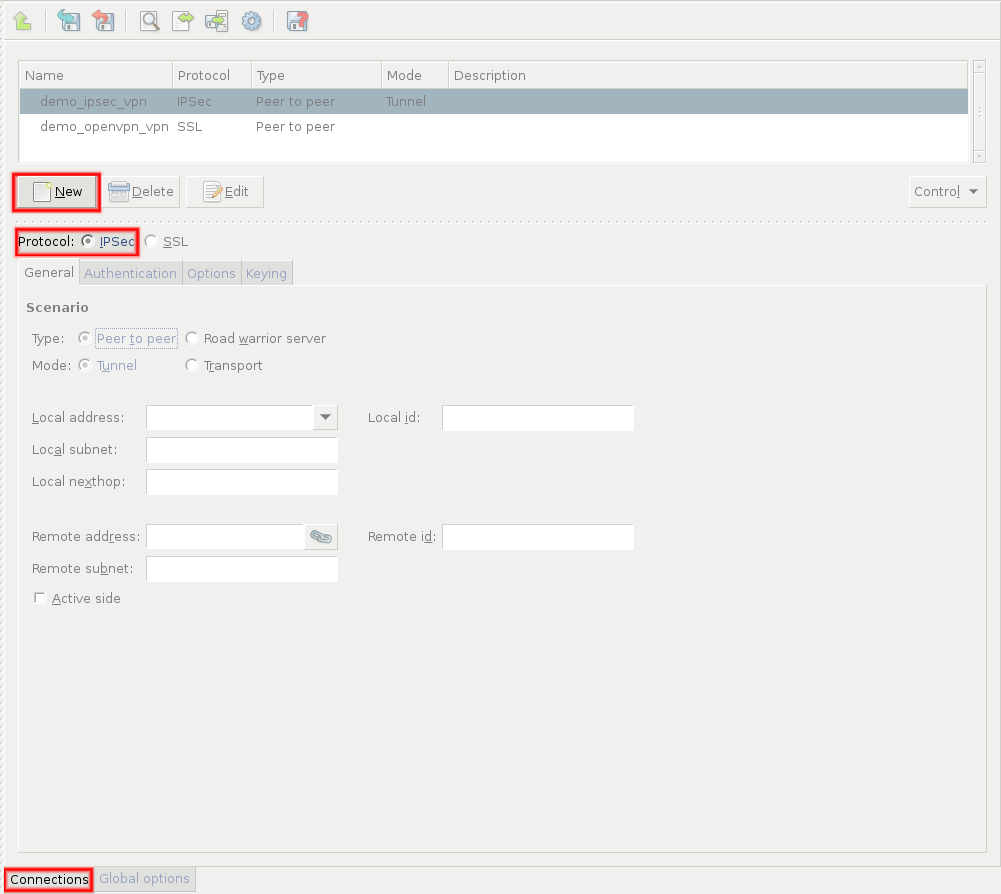
Click and enter a name for the connection.
Select the protocol option.
On the tab, set the VPN topology and the transport mode in the section.
To create a Peer-to-Peer connection, select the and the options.
To create a Peer-to-Network connection, select the and the options.
To create a Roadwarrior server, select the and the options.
To create a Network-to-Network connection, select the and the options.
Note When creating a Network-to-Network connection, the two endpoints of the VPN tunnel do NOT use the VPN to communicate with each other. To encrypt the communication of the endpoints, create a separate Peer-to-Peer connection.
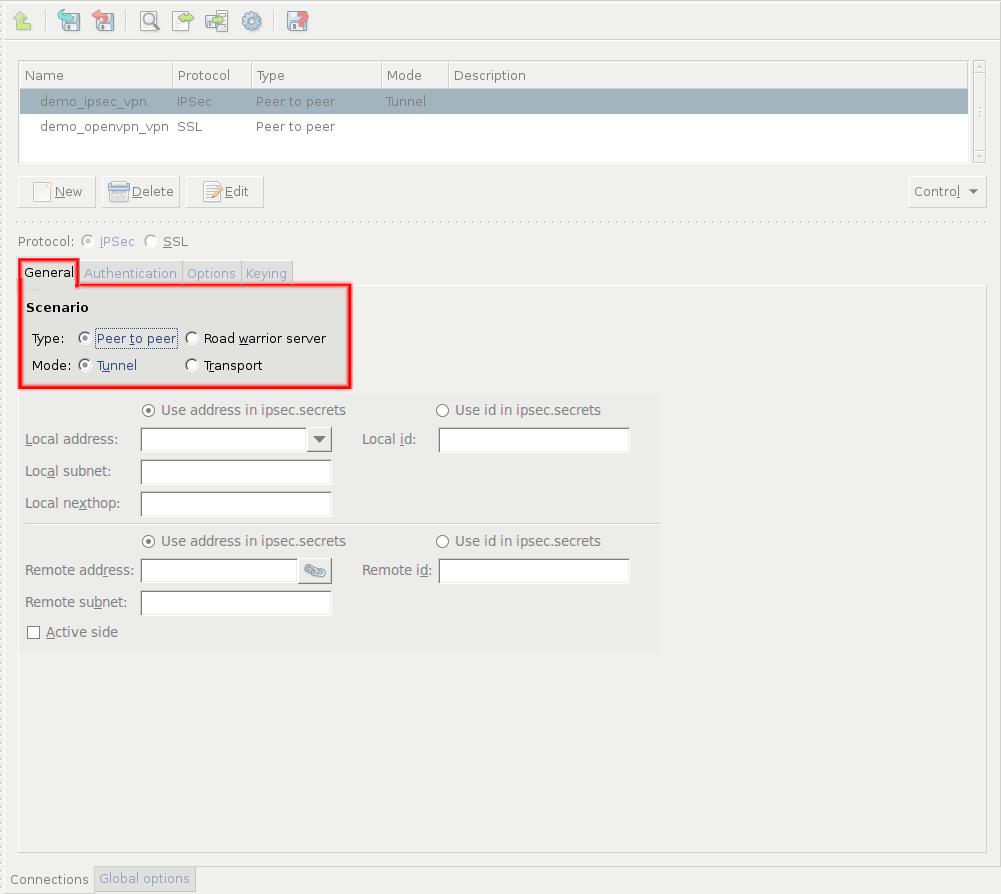
Configure the local networking parameters. These parameters affect the PNS endpoint of the VPN connection. Set the following parameters:
: Select the IP address that PNS will use for the VPN connection.
: The ID of the PNS endpoint in the VPN connection. Leave this field blank unless you experience difficulties in establishing the connection with the remote VPN application. If you set the , you might also want to set the option.
: The IP address of the default network gateway. Packets sent into the VPN tunnel are routed towards this gateway. This parameter defaults to the default gateway used by PNS.
: The subnet or zone protected by PNS that is permitted to use the VPN tunnel, or that can be accessed using the VPN tunnel. This option is available only for Peer-to-Network and Network-to-Network connections.
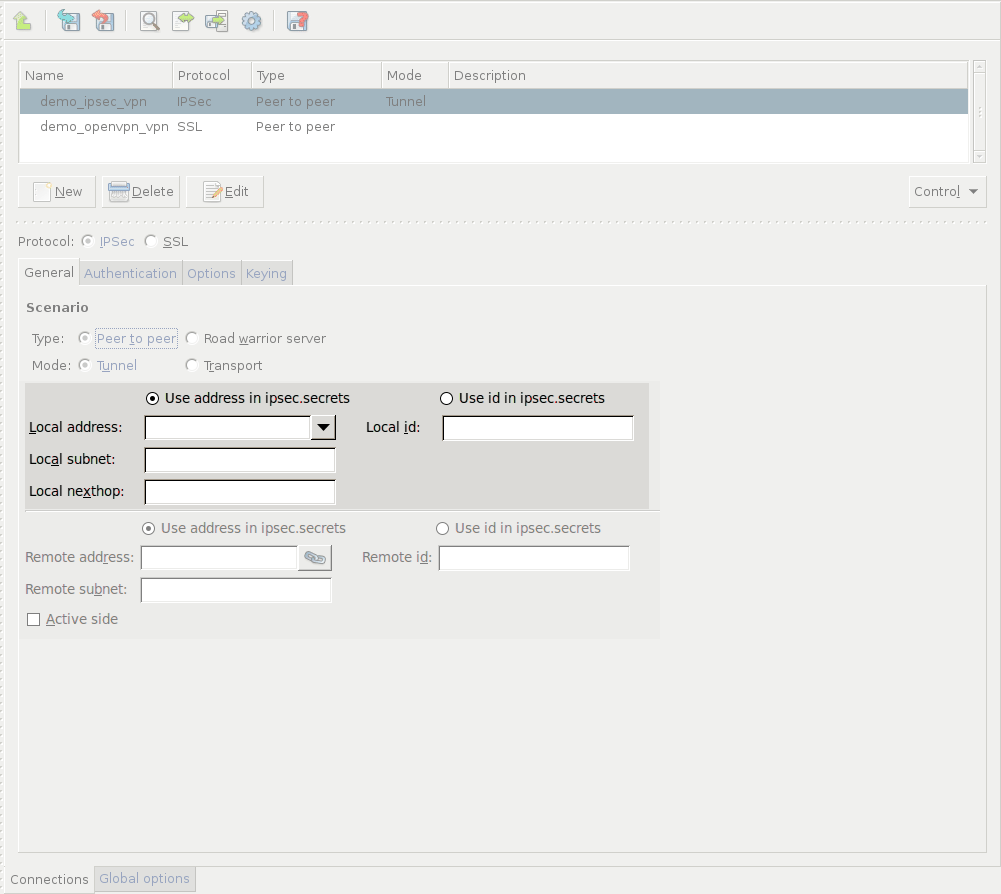
Configure the networking parameters of the remote endpoint. Set the following parameters:
: The IP address of the remote endpoint. Does not apply for roadwarrior VPNs.
: The ID of the remote endpoint in the VPN connection. Leave this field blank unless you experience difficulties in establishing the connection with the remote VPN application. If you set the , you might also want to set the option.
: The subnet or zone behind the remote endpoint that is permitted to use the VPN tunnel, or that can be accessed using the VPN tunnel. This option is available only for Peer-to-Network and Network-to-Network connections.
Note Network-to-Network connections connect the subnets specified in the and parameters.
Do not specify the subnet parameter for the peer side of Peer-to-Network connections, leave either the or the parameter empty.
When configuring Peer-to-Peer or Network-to-Network connections, select the option so that PNS initiates the VPN connection to the remote endpoint. If possible, enable this option on the remote endpoint as well.
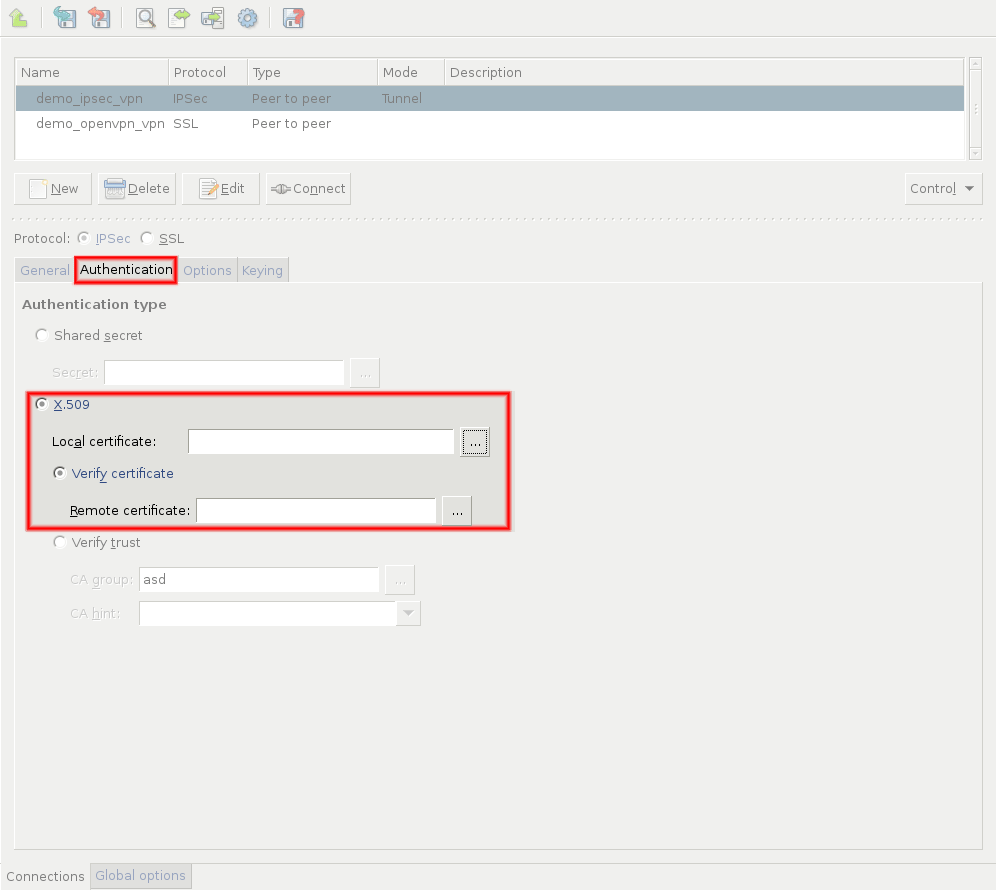
Click on the tab and configure authentication.
To use password-based authentication, select the option and enter the password in the field.
Note Authentication using a shared secret is not a secure authentication method. Use it only if the remote endpoint does not support certificate-based authentication. Always use long and complicated shared secrets: at least twelve characters containing a mix of alphanumerical and special characters. Remember to change the shared secret regularly.
To use certificate-based authentication, select the option and set the following parameters:
: Select a certificate available on the PNS host. PNS will show this certificate to the remote endpoint.
If the remote endpoint has a specific certificate, select the option and select the certificate from the field. PNS will use this certificate to verify the certificate of the remote endpoint.
If there are several remote endpoints that can connect to the VPN tunnel, select the option and select the trusted CA group containing the CA certificate of the CA that issued the certificates of the remote endpoints from the field. PNS will use this trusted CA group to verify the certificates of the remote endpoints. (See Section 11.3.7, Trusted CAs for details.)
PNS sends the common name of the accepted CAs to the remote endpoint, so the client knows what kind of certificate is required for the authentication. Select a specific CA certificate using the option if you want to accept only certificates signed by the selected CA.
Note See Chapter 11, Key and certificate management in PNS for details on creating and importing certificates, CAs, and trusted CA groups required for certificate-based authentication.
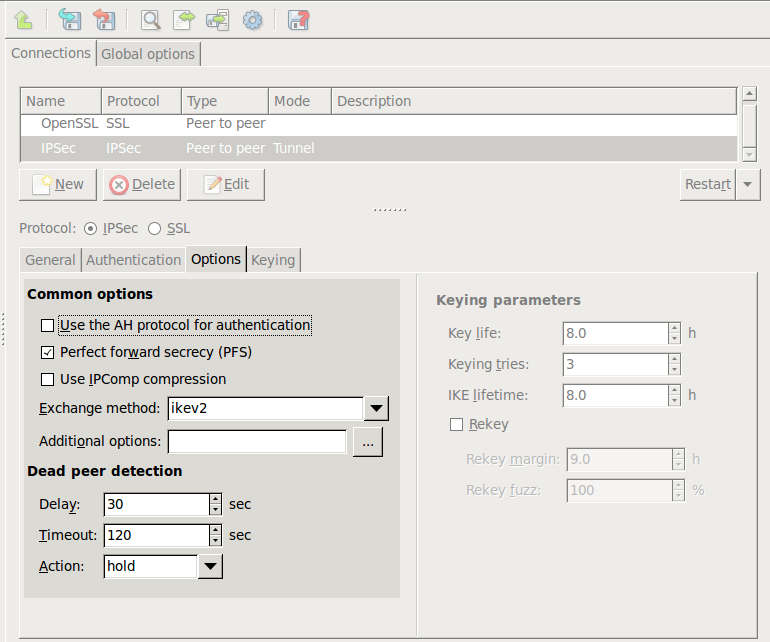
Click on the tab and set the parameter of to
restart. That way PNS attempts to restart the VPN connection if the remote endpoint becomes unavailable.Note Dead peer detection is effective only if enabled on both endpoints of the VPN connection.
Set other options as needed. See Section 16.3.2, IPSec options for details.
Note By default, PNS 3 F5 and later uses the IKEv2 key exchange protocol. However, earlier versions support only the IKEv1 protocol. Change the option to IKEv1 when the remote endpoint of the VPN connection is running PNS 3.4 LTS or earlier.
Published on June 04, 2020
© 2007-2019 BalaSys
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu