MC itself is just a graphical frontend to MS. It is MS that stores configuration information and manages connections with the agents on managed hosts. The MS-based firewall management can only be performed through MC; there is no console alternative. MC is not “bound” to a particular MS host, as long as the proper username/password pair is known, it can be used to connect to any MS host.
MC can be started the following way:
Windows: Locate the PNS folder in the menu and click on the icon. If no such folder has been created when MC was installed, start
zmc.exemanually from the installation folder.Linux: Start MC from the or menu of your desktop environment, or from the console by executing the following command: ./<installation-directory>/bin/zmc.
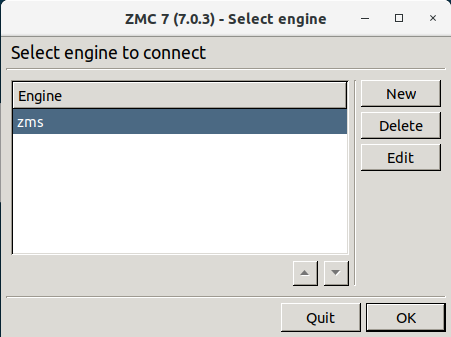
When you first start MC after the installation, the list of reachable MS hosts is empty, therefore you must define a new host. To define a new host, click . MC configurations are stored in a folder named .zmsgui. This folder (for the Windows version of MC) is created in the installing user's profile directory, which is typically %systemroot%\Documents and Settings\%username% The name of the file that stores MC configurations is zmsgui.conf. The Linux version of MC stores configuration information in the same manner, within the user's home directory.
Expected outcome:
After entering the correct password, if network connectivity is provided, the MC main screen greets you.
| Note |
|---|
When MC connects to a MS engine for the first time, it displays the SSH-style fingerprint of the MS host. During later connections, it checks the fingerprint automatically. |
| Warning |
|---|
MC and the MS to be accessed must have matching version numbers, that is, MS 7.0.1 must be accessed with MC 7.0.1. Login is not permitted if the version number of MS and MS is different. |
Published on June 04, 2020
© 2007-2019 BalaSys
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu