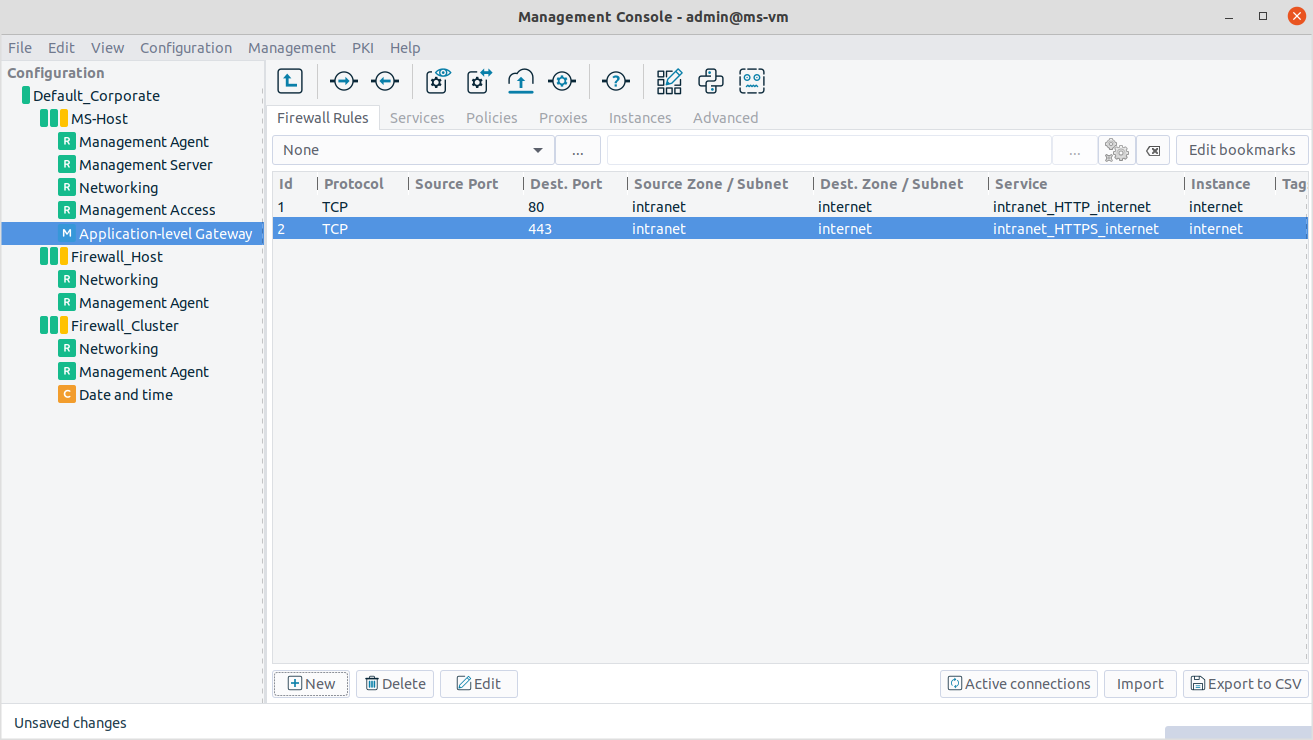
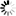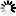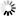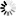Application-level Gateway firewall rules are managed on the page. The following information is displayed for every rule:
| Note |
|---|
Not every column is displayed by default. To show or hide a particular column, right-click on the header of the table and select the column from the menu. |
Whether a certain rule is active or not is visible by its colour, that is, it is dark-grey if the rule is active and it is light-grey if the rule is inactive.
: It is the unique ID number of the firewall rule.
: These are the tags (labels) assigned to the firewall rule. For details on assigning tags to rules, see Procedure 6.5.5, Tagging firewall rules.
: It is the transport protocol used in the connection. This is the protocol used in the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. For example, TCP, UDP, ICMP, and so on.
: The rule permits traffic only from the listed VPN connections (or IPSec connections with the specified Request ID).
: The rule permits traffic only for the clients of the listed zones and subnets.
: The rule permits traffic only for connections targeting the listed ports of the firewall host.
: The rule permits traffic only for connections that target addresses of the listed zones and subnets.
: The rule permits traffic only for connections that target an existing IP address of the selected interface (or interface group) of the firewall host. This parameter can be used to provide nontransparent service on an interface that received its IP address dynamically.
: The rule permits traffic only for connections that target the listed ports of the destination address.
: The name of the service is provided here used to inspect the traffic.
: The service started by the rule belongs to the instance shown.
: It provides a description of the rule.
: ICMP type determines what the ICMP packet is used for. If the type does not have any codes defined, the code field is set to zero.
Copyright: © 2021 Balasys IT Security
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu