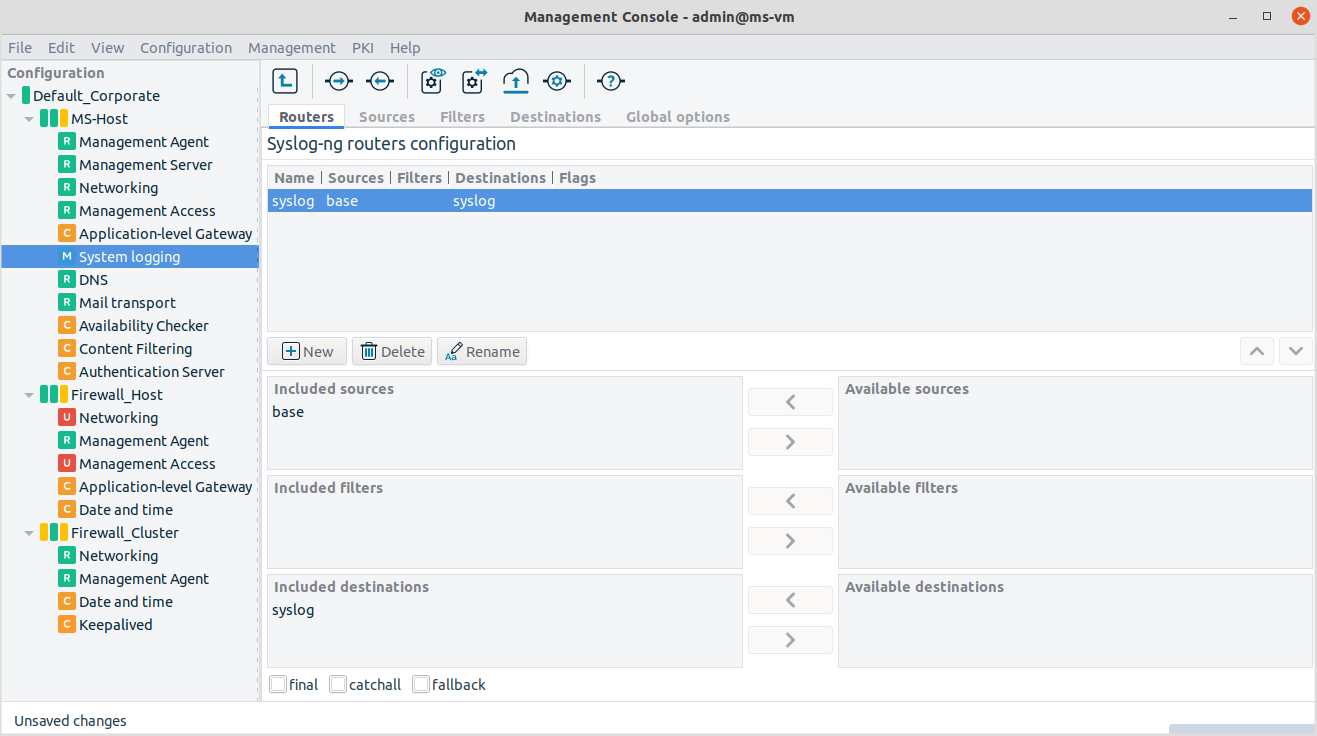
Logging rules are called Routers in syslog-ng terminology. Rules consist of a source, optionally a filter and a destination. The tab of the System logging component represents this philosophy well.
Just like sources, destinations and filters, more than one router can be present in the system. If you use several routers, it is recommended to apply a good naming strategy to easily identify the relevant log rules.
7.2.2.5.1. Procedure – Configure routers
To create a router click on .
Provide a name for the new router.
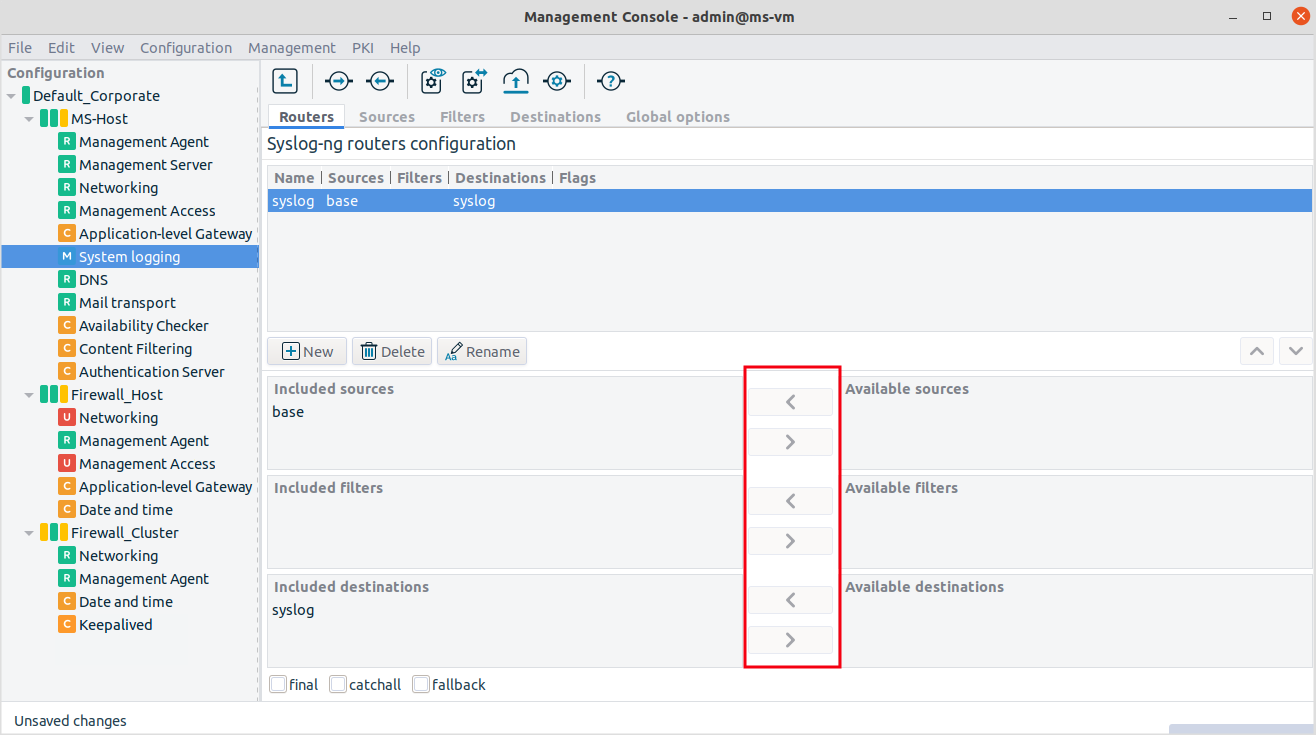
Select the components from the list of available sources, filters and destinations.
Example 7.2. Setting up a router If you select
baseas the source,postfixas the filter (optional, use the small arrow between the text boxes) andsyslogas the destination, the resulting router, that is, the log rule looks like this:log { source(s_base); filter(f_postfix); destination (d_syslog);flags ( ); };
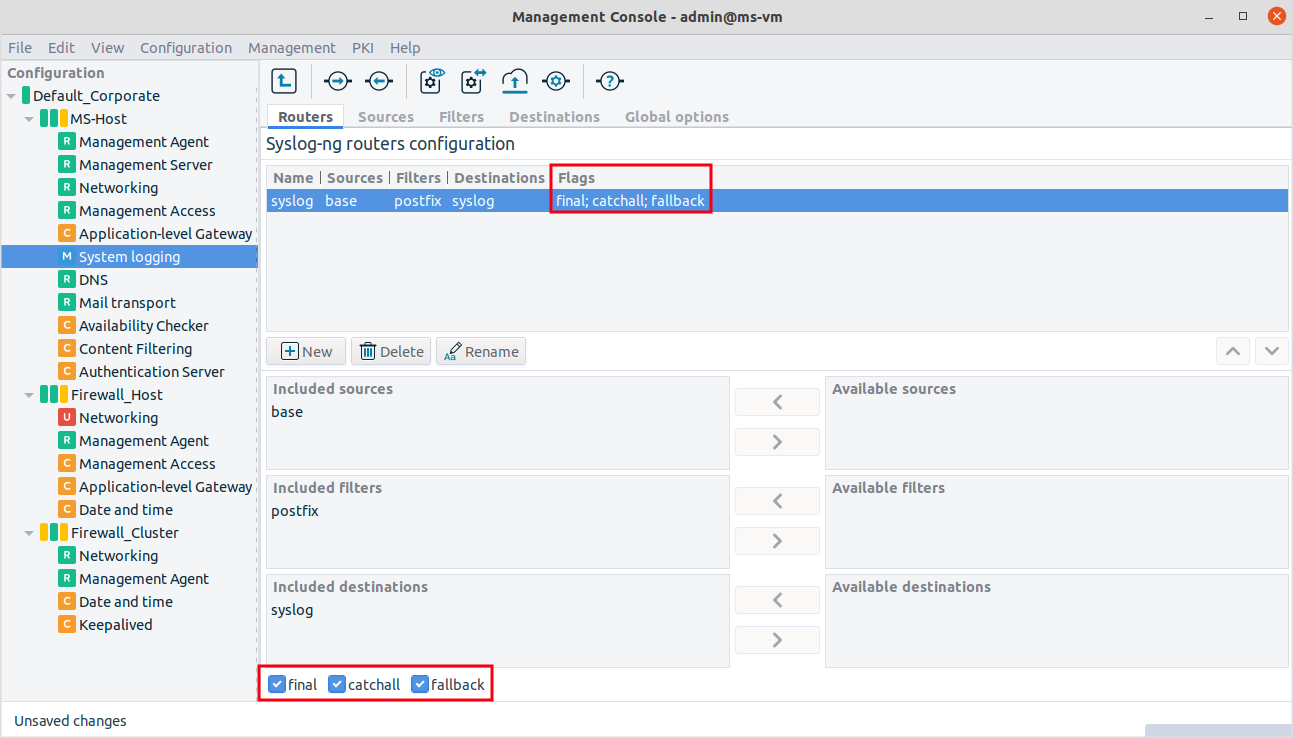
Specify flags for the router.
The flags component is empty. Use the checkboxes at the bottom to select the flag. Three possible flags are available.
Final flag means that the processing of log statements ends at this point.
Note Ending the processing of log statements does not necessarily mean that matching messages are stored once, as there can be matching log statements processed prior to the current one.
Fallback flag marks a log statement for 'fallback'. Defining a fallback statement means that only those messages are sent which do not match any 'non-fallback' log statements.
Catchall flag means that the source of the message is ignored, only the filters are taken into account when matching messages.
There are virtually endless possibilities for configuring a complex system logging architecture with syslog-ng. This chapter focused only on the basic concept and provided an architecture view including not only PNS and the MS host nodes, but presenting as well that the syslog-ng architecture can also include practically Unix/Linux machines.
For further information and details, see The syslog-ng Administrator Guide.
Copyright: © 2021 Balasys IT Security
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu