To modify instance parameters, select . The tab has the following parameters:
: Uncheck this option to inactivate the instance.
: The name of the instance.
: When renaming and instance and this option is enabled, Application-level Gateway stops the instance, renames it, then starts the renamed instance.
: The description of the instance.
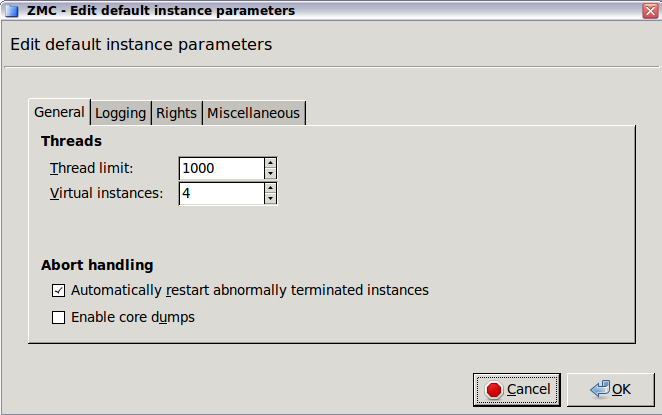
: The number of threads the instance can start. Set according to the anticipated number of concurrent connections. Most of the active client requests requires its own thread. If the is too low, the clients will experience delays and refused connection attempts.
: The number of Application-level Gateway processes the instance can start. This setting determines the number of CPU cores that the instance can use. If our PNS host has many CPUs, increase this value for instances that have high traffic. Note that the
Thread limitandThread stack limitparameters are apply separately for every process. For details on increasing the number of running processes, see Procedure 6.3.9, Increasing the number of running processes.For every process, Application-level Gateway uses a certain amount of memory from the stack. At most, a process uses the default value of the stack size of the host (which is currently 8 MB for Ubuntu 18.04 LTS). Application-level Gateway uses this memory only when it is actually needed by the thread, it is not allocated in advance.
: If enabled, Application-level Gateway automatically restarts instances that crash for some reason.
: If enabled, PNS automatically creates core dumps when a Application-level Gateway instance crashes for some reason. Core dumps are special log files and are needed for troubleshooting.
Published on June 04, 2020
© 2007-2019 BalaSys
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu