6.5.4. Procedure – Creating firewall rules
Purpose:
Firewall rules allow a specific type of traffic to pass the firewall. To create a new firewall rule, complete the following steps.
Steps:
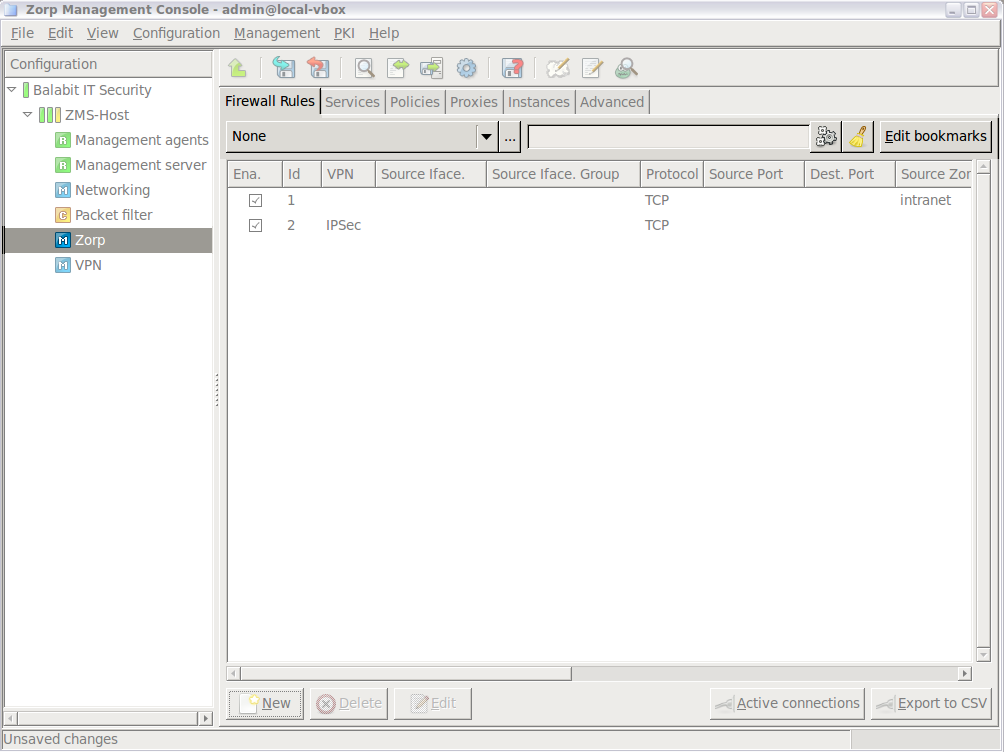
Login to MS and select . A new window opens.
Select the tab.
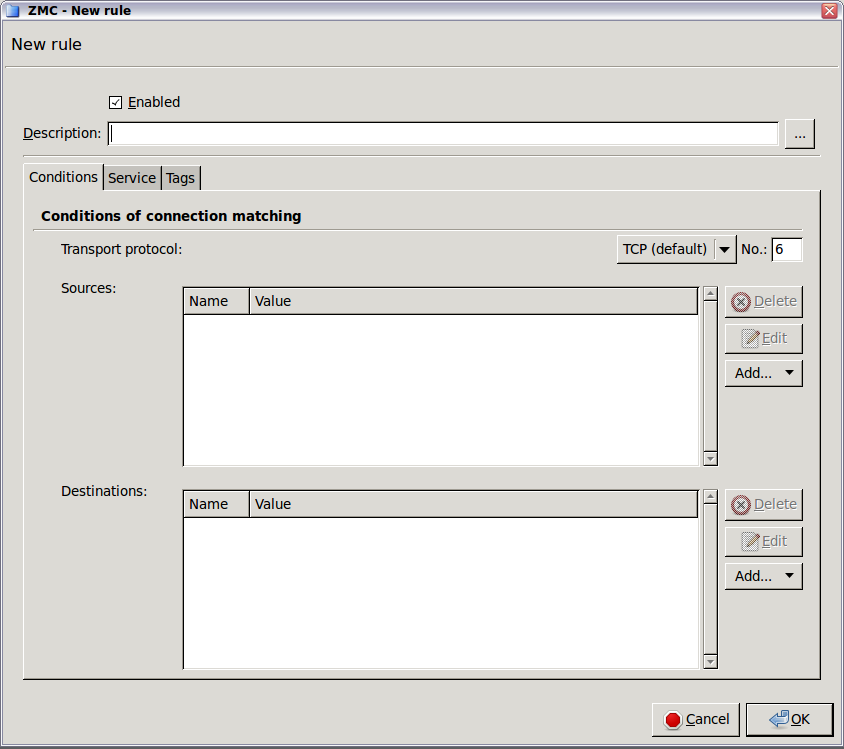
Select the used in the connection. This is the protocol used in the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. The following protocols are supported:
TCP,UDP,ICMP,IGMP,DCCP,GRE,ESP,AH,SCTP, andUDP-Lite.To permit both TCP and UDP traffic, select .
To permit any Layer 4 protocol, select .
For ICMP traffic, you can specify the permitted type and subtype (code) as well.
Select the sources. Application-level Gateway can limit the traffic that can pass the firewall only to traffic that comes from selected source networks. To permit traffic only from specific networks, select . You can select zones, IPv4 or IPv6 subnets, interfaces, interface groups, and ports. Use always the most specific source suitable for your rule.
Note To specify multiple ports, separate the ports with a comma, for example:
80,443To specify a port range, use a colon, for example:
2000:2100To specify multiple port ranges, separate the port ranges with commas, for example:
2000:2100,2200:2400.Select the destinations. Application-level Gateway can limit the traffic that can pass the firewall only to traffic that is targeting selected destination addresses. To permit traffic only to specific networks, select . You can select zones, IPv4 or IPv6 subnets, interfaces, interface groups, and ports. Use always the most specific destination suitable for your rule.
Note For rules that start nontransparent services, set the destination address and the port to an address of the firewall host.
Note To specify multiple ports, separate the ports with a comma, for example:
80,443To specify a port range, use a colon, for example:
2000:2100To specify multiple port ranges, separate the port ranges with commas, for example:
2000:2100,2200:2400.Note Starting with Application-level Gateway 3 F5, it is not mandatory to set the sources and destinations. Sources and destinations act as a filter, they limit access to the clients or servers of the sources and destinations. A firewall rule without sources and destinations acts as a rule that simply forwards traffic between any client and destination.
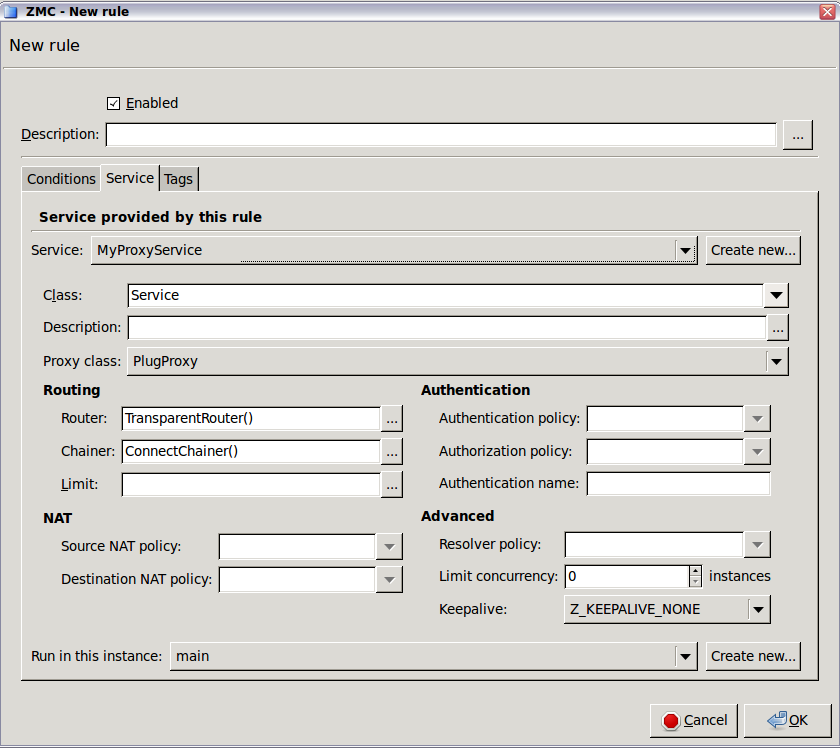
Select the service to use. Select and select the service to start for connections matching the rule. The service determines type of traffic that will be permitted by this rule (for example, HTTP, FTP, and so on) and also the level the traffic will be inspected (application or packet-filter level).
Note Proxy services can be used only if the option is set to
TCP,UDP, orTCP or UDP.Warning The settings and parameters of the service shown on the tab of the rule are for reference only. Do not modify them, because it might interfere with other rules using the same service. To modify the parameters of a service, or to create a new service, use the tab of the MC component.
Select the instance the service should run in.
Optional Step: By default, new rules become active when the configuration is applied. To create a rule without activating it, deselect the option of the rule.
Optional Step: To limit the number of connections that can be started by the rule, configure rate limits for the connections. For details, see Procedure 6.5.7, Connection rate limiting.
Click , then commit your changes.
Expected result:
A new firewall rule is created and added to the list of firewall rules. If the rule is active, the traffic specified in the rule can pass the firewall.
Published on June 04, 2020
© 2007-2019 BalaSys
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu