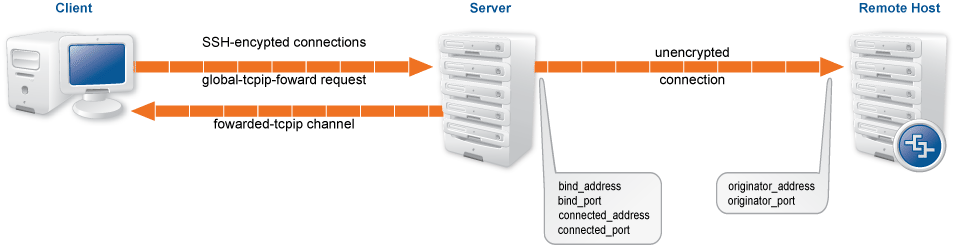
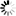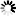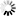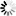Remote port-forwarding transfers connections arriving to a port of
the server to the client. The client sends a
global-tcpip-forward request to the server.
The parameters of this request tell the server which address and
port it should listen on for incoming connections (
bind_address, bind_port).
When the server receives a connection to this address/port pair,
it opens a forwarded-tcpip towards the client.
The parameters of these requests are summarized in the following tables.
| global-tcpip-forward | |
|---|---|
| Connections arriving to the specified IP address and port of the server are forwarded to the client. | |
| bind_address | The server forwards connections received on this address to the client. The following special addresses may be used:
|
| bind_port | The server forwards connections received on this port to the client. |
| forwarded-tcpip | |
|---|---|
| Opens a channel used to forward remote connections to the client. | |
| connected_addr | The IP address of the server that received the connection. |
| connected_port | The port of the server that received the connection. |
| originator_addr | The IP address of the remote host whose connection is forwarded to the client. |
| originator_port | The port of the remote host whose connection is forwarded to the client |
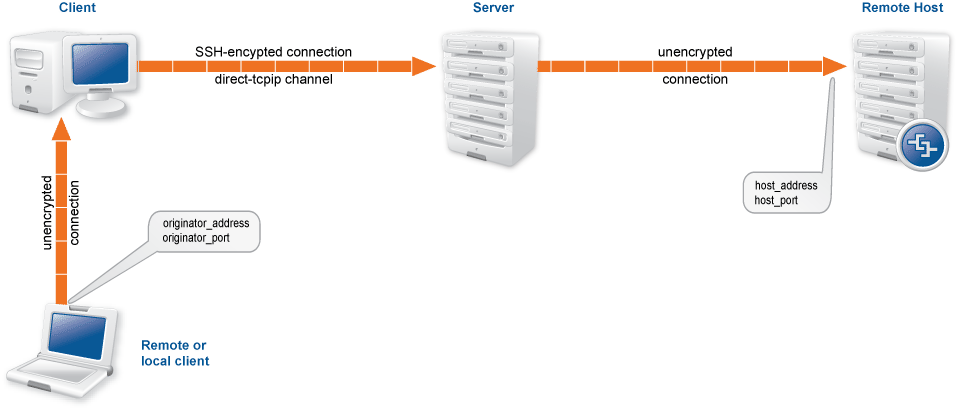
Local port-forwarding transfers connections arriving to the client
from a host to a remote host via the SSH server. For local port-forwarding,
the client sends a
direct-tcpip channel opening request to the
server. The parameters of this request tell the server which host it should
forward the connection, as well as the address of the host that connects to the client
(usually localhost).
This request has the following parameters.
| direct-tcpip | |
|---|---|
| Opens a channel used to forward remote connections to the client. | |
| originator_addr | The IP address of the host whose connection is forwarded to the remote host. |
| originator_port | The port of the host whose connection is forwarded to the remote host. |
| host_addr | The IP address of the remote host that is the destination of the forwarded connection. |
| host_port | The port of the remote host that is the destination of the forwarded connection. |
| Example 4.47. Restricting local forwarding |
|---|
|
The following proxy class permits local forwading only
to port class RestrictedlocalforwardSshProxy(SshProxy):
def config(self):
SshProxy.config(self)
self.client_channel["session"] = (SSH_CHAN_ACCEPT)
self.client_channel["direct-tcpip"] = (SSH_CHAN_ACCEPT)
self.client_request["direct-tcpip"] = (SSH_REQ_POLICY, self.controllocalforward)
self.client_channel["*"] = (SSH_CHAN_REJECT)
def controllocalforward(self, side, index, request):
if request.host_address == "192.168.1.1" and request.host_port == "80":
return SSH_REQ_ACCEPT
return SSH_REQ_REJECT
|
Published on June 04, 2020
© 2007-2019 BalaSys
Send your comments to support@balasys.hu